DIN vs JIS vs ISO Standards for Collated Construction Screws Guide for Distributors
- Collated Screws, Construction Screws
Nearly 65% of construction project delays stem from incompatible fastener systems that require last-minute replacements or modifications. This statistic highlights a critical issue facing distributors of construction screws across North America and Europe. As global supply chains become increasingly interconnected, understanding the differences between international standards for collated construction screws has never been more important.
Table of Contents
When your customers need to complete structural framing quickly and efficiently, the compatibility between their automatic screw guns and your fastener products can make or break project timelines. This guide will help you navigate the complex world of DIN, JIS, and ISO standards for collated construction screws, ensuring you provide the right products for your market’s specific requirements.
What Are Collated Construction Screws?
Collated screws represent one of the most significant advancements in construction fastener technology over the past three decades. These specially packaged fasteners are designed for automatic feeding into power tools, dramatically increasing installation efficiency compared to traditional loose screws.
The evolution of collated construction screws began in the 1980s when manufacturers sought ways to improve productivity in commercial construction. Today, they’re essential components in residential and commercial construction alike.
These fasteners come in three primary collation formats:
- Strip collation: Linear strips typically holding 25-50 screws, ideal for framing and decking applications
- Coil collation: Spiral-wound configurations containing 100+ screws, commonly used for subfloor and roofing applications
- Magazine collation: Box-like containers designed for specialized tools in high-volume applications
The advantages of self tapping screws in collated form include:
- Installation speeds 3-5 times faster than loose screws
- Consistent driving depth and torque application
- Reduced worker fatigue and repetitive motion injuries
- Fewer dropped or wasted fasteners
- Simplified inventory management on job sites
For large-scale projects, contractors using collated construction screws with auto-feed systems can install up to 1,200 screws per hour—a productivity gain that translates directly to project cost savings.
DIN Standards for Collated Construction Screws
The Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) has established comprehensive standards that have traditionally dominated European construction markets, particularly in Germany and neighboring countries. When working with European distributors, you’ll frequently encounter references to DIN standards for self drilling screws and other collated fasteners.
Key DIN Standards Applicable to Collated Construction Screws
DIN standards relevant to collated construction screws include:
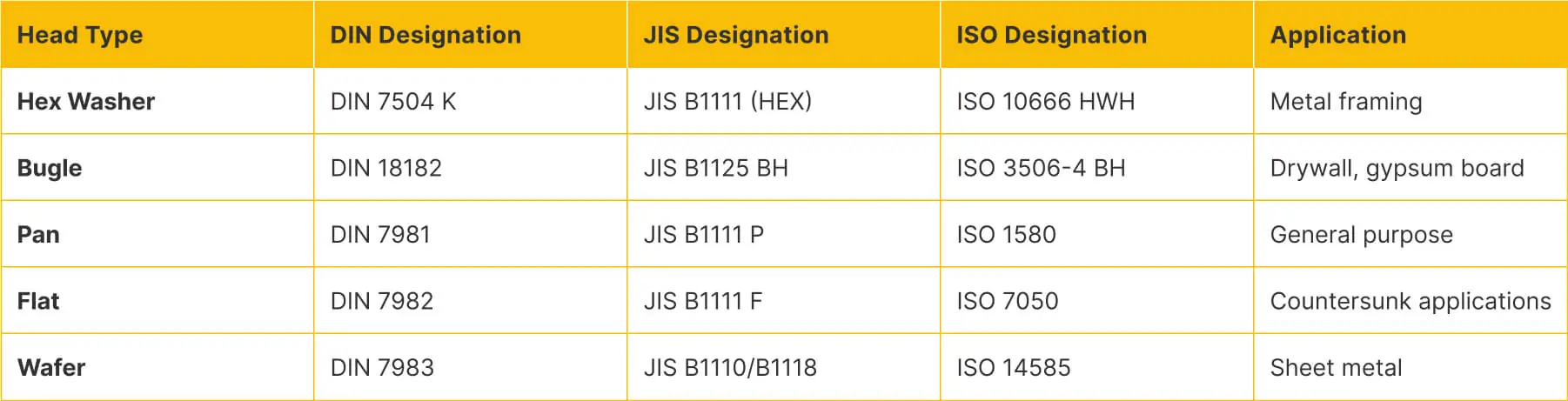
DIN standards specify precise thread profiles with mostly coarse metric threads ranging from M3.5 to M6 for construction applications. The most common head types include:
- Hex washer heads (HWH)
- Pan heads
- Wafer heads
- Bugle heads for drywall applications
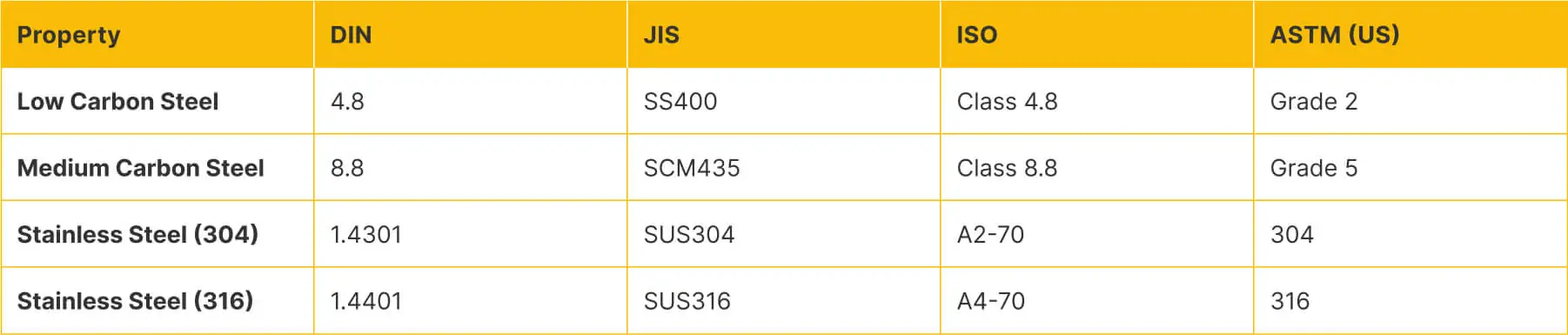
Material specifications under DIN classifications typically reference:
- Low-carbon steel (DIN 4.8) for interior applications
- Stainless steel (DIN 1.4301, equivalent to AISI 304) for exterior or corrosive environments
DIN tolerances follow the ISO fit class system, with 6g for external threads and 6H for internal threads being the most common specifications for construction fasteners.
JIS Standards for Collated Construction Screws
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) system provides specifications widely used throughout Asia and increasingly recognized in global markets. For distributors sourcing Type 17 screws and other collated fasteners from Asian manufacturers, understanding JIS requirements is essential.
JIS standards feature some distinctive characteristics compared to their DIN and ISO counterparts:
JIS Specifications for Construction Fasteners
- JIS B1111: General purpose metric screws
- JIS B1112: Tapping screws
- JIS B1125: Drilling screws
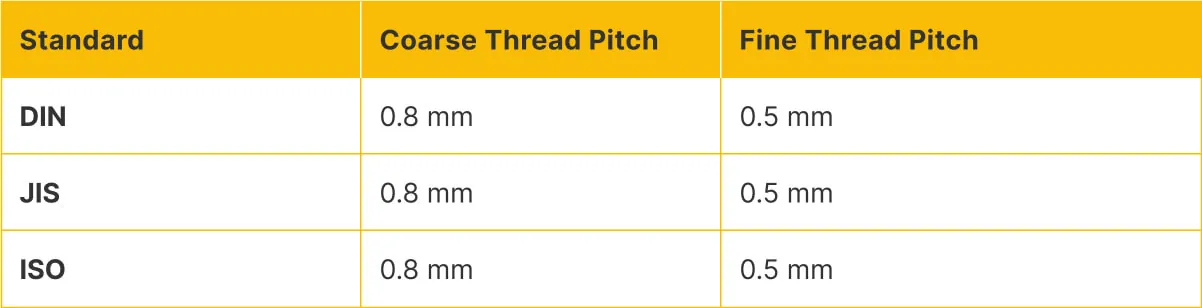
One of the most notable differences in JIS standards is the thread pitch specification. JIS often utilizes finer thread pitches than comparable DIN standards. For example:
JIS standards also feature unique drive system specifications, particularly the JIS B1012 cross-recess drive, which appears similar to Phillips but has slightly different geometry. This subtle difference can lead to unexpected issues when using Phillips drivers with JIS screws.
Common head styles under JIS include:
- Binding heads
- Truss heads
- Pan heads
- Hex washer heads
Materials are typically specified using JIS designations:
- SS400 (equivalent to ASTM A36 carbon steel)
- SUS304 (equivalent to AISI 304 stainless steel)
- SUS316 (equivalent to AISI 316 stainless steel)
When sourcing chipboard screws or other collated fasteners from manufacturers using JIS standards, always confirm cross-compatibility with your market’s tool systems.
ISO Standards for Collated Construction Screws
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed globally recognized standards that increasingly serve as common ground between different regional specifications. For distributors looking to simplify their supply chains, ISO-compliant roofing screws and other collated fasteners offer significant advantages.
Primary ISO Standards for Collated Construction Screws
The most relevant ISO standards include:
- ISO 10666: Technical specifications for drilling screws
- ISO 898-1: Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel
- ISO 3506: Mechanical properties of corrosion-resistant stainless steel fasteners
- ISO 4042: Electroplated coatings
- ISO 6789: Assembly tools for screws and nuts
The adoption of ISO standards has gained significant momentum in both North American and European markets, providing several key benefits:
- Simplified procurement: Reduced need for market-specific inventories
- Global compatibility: Increased interchangeability between different manufacturers’ systems
- Consistent quality parameters: Standardized testing methodologies
- Clear marking requirements: Improved traceability throughout the supply chain
ISO dimensional specifications establish harmonized thread pitches and tolerances that bridge the differences between traditional DIN and JIS systems. This harmonization is particularly valuable for drywall screws and other high-volume collated fasteners.
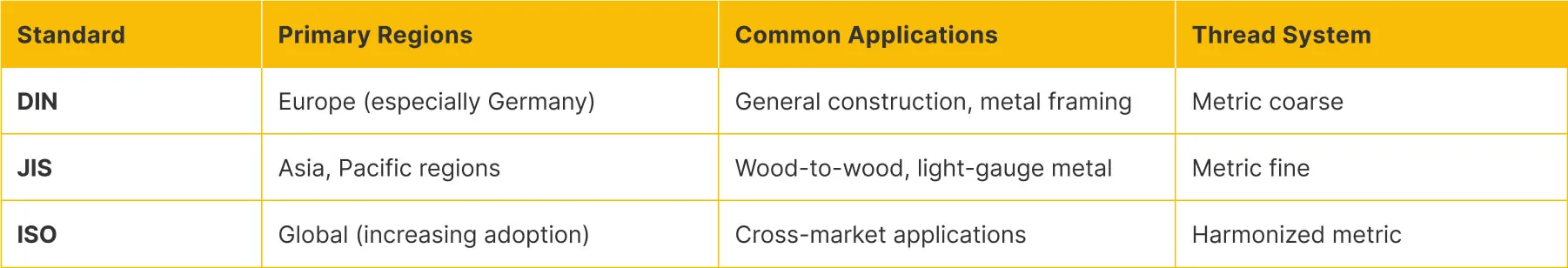
Side-by-Side Comparison of International Standards
Understanding the relationships between these three standards systems helps distributors make informed decisions when specifying collated construction screws for different markets.
Thread System Comparison by Region
Head Types Across Standards
Different head designs serve specific functional purposes and are referenced differently across standards:
Thread Pitch Comparison for M5 Fasteners
While there is nominal alignment in M5 thread specifications, actual manufacturing tolerances may differ between standards, potentially causing fit issues in precision applications.
Material Grade Equivalents
When sourcing concrete screws and other specialized collated fasteners, understanding material equivalencies is crucial:
How to Specify the Right Standard for Your Market
Selecting the appropriate standard for collated construction screws requires understanding regional preferences and application requirements. For stainless steel screws and other premium fasteners, this becomes especially important.
North American Market Considerations
In North America, while traditional Imperial measurements still appear in some applications, ISO metric standards have gained significant traction, particularly for commercial construction. When supplying North American distributors:
- Specify full ISO standard references (e.g., “ISO 10666-2017 M3.5×35 P0.6”)
- Request mill certificates for material verification
- Note that legacy UNC/UNF threading may still be required for certain renovation projects
- Be aware that head styles may follow ASME rather than ISO conventions
European Market Considerations
European markets generally follow DIN or harmonized EN-ISO standards:
- Provide DIN references for German markets (still preferred despite ISO harmonization)
- Use EN-ISO designations for broader European distribution
- Include thread class specifications (6g/6H being most common)
- Note regional coating preferences (zinc vs. zinc-nickel vs. geomet)
Practical Documentation Tips
To avoid miscommunication and ensure compatibility:
- Always include complete screw specifications in your documentation
- Specify both thread class and head style explicitly
- Reference material properties according to the standard used in the target market
- Provide conversion tables when supplying across different standard regions
Quality Control for International Standard Compliance
Ensuring that your collated construction screws meet the specified standards requires robust quality control procedures. Establishing clear verification protocols protects both distributors and end-users from costly compatibility issues.
Essential Quality Verification Steps
Physical Inspection
- Thread gauge verification against standard-specific requirements
- Head dimension conformance testing
- Drive compatibility checks with standard tools
- Coating thickness measurement
Documentation Requirements
- Request 3.1 material test reports under EN 10204 for critical applications
- Verify manufacturer’s ISO 9001 quality management certification
- Confirm collation specifications match tool system requirements
- Review torque testing results against specified standard
Ongoing Quality Assurance
- Implement batch marking for traceability
- Retain samples from each shipment for 6 months minimum
- Conduct regular supplier audits focusing on collating equipment calibration
- Test random samples from each lot for dimensional accuracy and performance
For distributors maintaining extensive inventories, creating a standards cross-reference database can prevent mix-ups and ensure that customers receive products compliant with their regional expectations.
Ensuring Project Success with Standard-Compliant Fasteners
Nearly 80% of project managers cite fastener reliability as a critical factor in meeting construction deadlines. By providing collated construction screws that precisely match your customers’ regional standards and tool systems, you position your distribution business as a trusted partner rather than just a supplier.
The investment in understanding DIN, JIS, and ISO standards pays dividends through:
- Reduced returns and warranty claims
- Strengthened customer relationships
- Expanded market opportunities
- Enhanced reputation for technical expertise
For customized collated screw solutions optimized for your specific market needs, Cheng Hao’’s technical team offers comprehensive standard compatibility assessments and specialized manufacturing capabilities. Contact us to discuss how our expertise in international fastener standards can support your distribution business.